JOINT PAIN
We use a team approach to providing health care, and involve the patient as part of our team. Involvement by our staff in the community.
What is OsteoArthritis?
Osteoarthritis (OA)
It is a frequent degenerative joint disease that especially impacts the cartilage, which is the slippery tissue that covers the ends of bones in a joint. It can happen in any joint; however frequently influences the knees, hips, hands, and spine. Here’s an overview of its causes, symptoms, and prevention:
Causes:
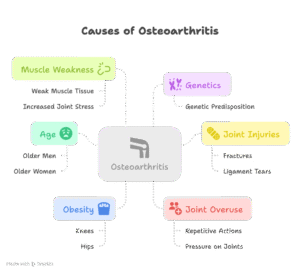
-Age:
OA is extra frequent in older men and women as wear and tear on the joints accumulate over time.
- -Genetics:
- There can be a genetic predisposition to growing osteoarthritis.
- –Joint Injuries:
- Previous joint injuries, such as fractures or ligament tears, can increase the risk of OA in the affected joint.
- -Obesity:
- Excess body weight places stress on weight-bearing joints, mainly the knees and hips.
- –Joint Overuse:
- Repetitive actions or things to do that put pressure on a joint can contribute to OA.
- –Muscle Weakness:
- Weak muscle tissue around the joint may additionally fail to provide enough support, main to increased stress on the joint.
Symptoms: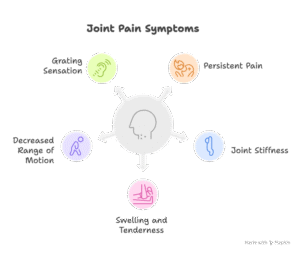
1. Pain:
Persistent joint pain regularly worsened with motion and was relieved with rest.
2. Stiffness:
Joint stiffness, mainly after durations of inaction or upon waking in the morning.
3. Swelling:
Swelling and tenderness around the affected joint.
4. Decreased Range of Motion:
Difficulty in shifting the joint via its full range of motion.
5. Grating Sensation:
A grating sensation or the sound of bone rubbing on bone throughout joint movement.
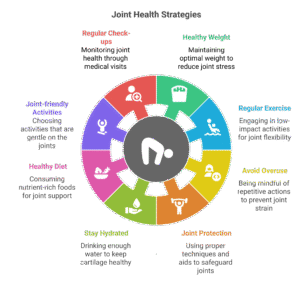
Prevention:
-Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Managing body weight can minimize stress on weight-bearing joints.
-Exercise Regularly:
Engage in minimal impact exercises, such as swimming or walking, to toughen muscle groups and enhance joint flexibility.
-Avoid Joint Overuse:
Be conscious of repetitive things to do that can also stress the joints.
-Use Joint Protection Techniques:
Practice suited physique mechanics and use assistive units if wished to guard joints at some point of each day activities.
-Stay Hydrated:
Drink sufficient water to preserve the cartilage hydrated and functioning properly.
-Healthy Diet:
Consume a balanced food plan rich in nutrients, especially those that help joint health.
-Joint-friendly Activities:
Choose things to do that are mild on the joints, such as biking or yoga.
-Regular Check-ups:
Regular clinical check-ups can assist in early detection and the management of joint problems.
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
It is a persistent autoimmune disease that chiefly impacts the joints, main to inflammation, pain, and irreversible joint damage.
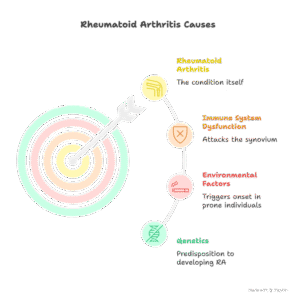
Causes:
The precise purpose of rheumatoid arthritis is no longer known; however, it is believed to result from an aggregate of genetic and environmental factors. Some elements that may additionally make a contribution to the improvement of RA include:
-Genetics: There is a genetic predisposition, as humans with a family history of rheumatoid arthritis are extra probably to develop the condition.
-Environmental Factors: Certain environmental factors, such as infections, smoking, and hormonal changes, may additionally set off the onset of rheumatoid arthritis in genetically prone individuals.
In RA, the immune system mistakenly assaults the synovium (the lining of the membranes that encompass the joints), main to infection and joint damage.
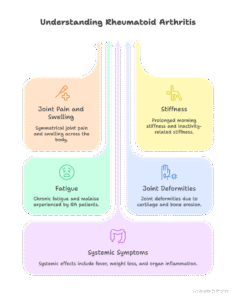
Symptoms:
1. Joint Pain and Swelling: RA normally impacts joints on all aspects of the body, regularly in a symmetrical pattern. The joints are painful, swollen, and may additionally experience warmth.
2. Stiffness: Morning stiffness lasting for numerous hours is a frequent symptom. Stiffness may also additionally happen after intervals of inactivity.
3. Fatigue: Many humans with RA experience chronic fatigue and an everyday feeling of malaise.
4. Joint Deformities: Over time, RA can lead to joint deformities and loss of function. This is the end result of the erosion of cartilage and bone.
5. Systemic Symptoms: RA can have an effect on organs and structures at some stage in the body, main to signs and symptoms such as fever, weight loss, and infection in different organs.
Prevention:
Currently, there is no recognized way to forestall rheumatoid arthritis completely. However, some lifestyle adjustments and techniques might also assist in limiting the risk or controlling symptoms:
-Healthy Lifestyle: Adopting a healthful lifestyle, consisting of everyday exercising and a balanced diet, may additionally make a contribution to average well-being and might also have a tremendous impact on joint health.
-Avoiding Smoking: Smoking has been recognized as a dangerous thing for RA, so heading off or quitting smoking might also be beneficial.
-Early Diagnosis and Treatment: Early detection and on-the-spot therapy can assist manipulate signs and sluggish the development of the disease, undoubtedly stopping joint damage.
-Regular Check-ups: Regular scientific check-ups can help display your fitness and become aware of any signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis or different autoimmune conditions early on.
What is Cervical Pain?
Cervical pain
It additionally recognised as neck pain, refers to pain or ache in the location of the cervical spine positioned in the neck. It can be prompted by means of more than a few factors, and its symptoms, prevention, and cure choices may additionally vary.
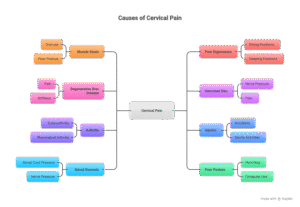 Causes of Cervical Pain:
Causes of Cervical Pain:
-Muscle Strain: Overuse or poor posture can lead to muscle stress in the neck.
-Poor Ergonomics: Incorrect sitting or sound asleep positions, particularly when the use of digital devices, can contribute to cervical pain.
-Degenerative Disc Disease: Wear and tear on the discs between vertebrae can result in pain and stiffness.
-Herniated Disc: When the gentle internal fabric of a disc protrudes, it can press on nerves, inflicting pain.
-Arthritis: Conditions like osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis can have an effect on the neck joints.
-Injuries: Trauma from accidents or sports activities may also cause cervical pain.
-Spinal Stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal can put stress on the spinal cord and nerves.
-Poor Posture: Prolonged intervals of bad posture, such as hunching over a computer, can pressure the neck.
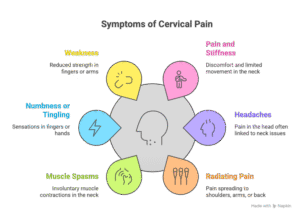 Symptoms of Cervical Pain:
Symptoms of Cervical Pain:
1. Pain and Stiffness: Discomfort or ache in the neck, frequently accompanied by stiffness.
2. Headaches: Cervicogenic headaches can contribute to anxiety headaches.
3. Radiating Pain: Pain that may additionally radiate into the shoulders, arms, or top back.
4. Muscle Spasms: Involuntary muscle contractions in the neck.
5. Numbness or Tingling: These sensations may also be felt in the fingers or hands.
6. Weakness: Weakness in the fingers or arms might also happen in extreme cases.
Prevention of Cervical Pain:
-Maintain Good Posture: Be conscious of your posture, in particular when sitting or the usage of digital devices.
-Ergonomics: Ensure that your workspace is set up ergonomically to guide an impartial backbone position.
-Regular Breaks: Take breaks to stretch and move, specifically for the duration of lengthy periods of sitting or laptop use.
-Exercise: Strengthening and stretching workout routines for the neck and top lower back can help stop pain.
-Sleeping Position: Use a supportive pillow and mattress, and keep an acceptable snoozing position.
-Avoid Tension: Manage stress and anxiety via rest strategies or activities.
-Stay Active: Regular bodily recreation helps preserve usual spinal health.
What is Gout?
Gout
It is a kind of arthritis that takes place when there is a buildup of uric acid in the blood, main to the formation of crystals in the joints. These crystals can cause surprising and extreme pain, inflammation, and swelling in the affected joints. The most frequently affected joint with the aid of gout is the big toe; however, it can additionally affect different joints such as the ankle, knee, elbow, wrist, and fingers.
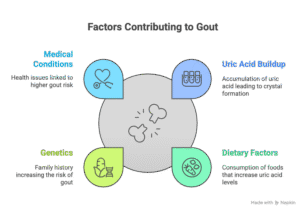
Causes of Gout:
1. Uric Acid Buildup: Gout is particularly caused by an accelerated degree of uric acid in the blood. Uric acid is a waste product that is usually excreted via urine. When the body produces too much uric acid or fails to excrete it properly, it can lead to the formation of urate crystals in the joints.
2. Dietary Factors: Certain meals and drinks, such as pink meat, seafood, alcohol (especially beer), and sugary drinks, can make contributions to the buildup of uric acid.
3. Genetics: A household history of gout can amplify the chance of developing the condition.
4. Medical Conditions: Conditions such as kidney disease, excessive blood pressure, and diabetes can be related to an elevated hazard of gout.
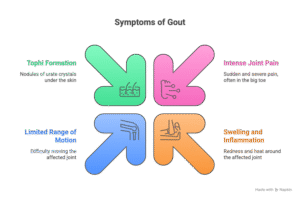
Symptoms of Gout:
-Intense Joint Pain: Gout generally reasons unexpected and extreme pain, frequently beginning in the center of the night. The ache is most often felt in the massive toe, however can have an effect on different joints.
-Swelling and Inflammation: The affected joint will become swollen, red, and hot to the touch.
-Limited Range of Motion: Due to pain and swelling, the range of motion in the affected joint might also be limited.
-Tophi Formation: In persistent cases, small, tough nodules referred to as tophi can also increase beneath the pores and skin around joints or on the earlobe. These are deposits of urate crystals.
Prevention and Management:
-Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a wholesome lifestyle can assist in preventing and managing gout. This consists of retaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, limiting alcohol consumption (especially beer), and avoiding high-purine foods.
-Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can minimize the risk of gout, as extra body weight is related to greater levels of uric acid.
-Limiting Purine-rich Foods: Foods excessively rich in purines, such as organ meats, purple meat, and certain seafood, ought to be consumed in moderation.
